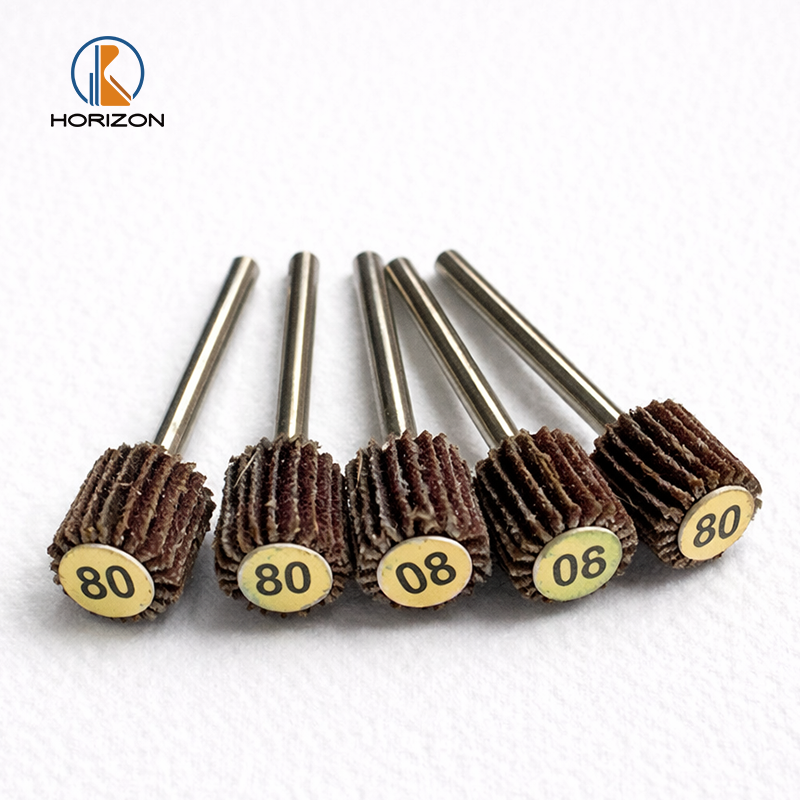
Цилиндрические лепестковые круги
- Главная
- Цилиндрические лепестковые круги
Категории
Цилиндрические лепестковые круги
Обзор продукта
Радиальные лепестки на цилиндрическом сердечнике — для равномерного контакта и плавного блендинга
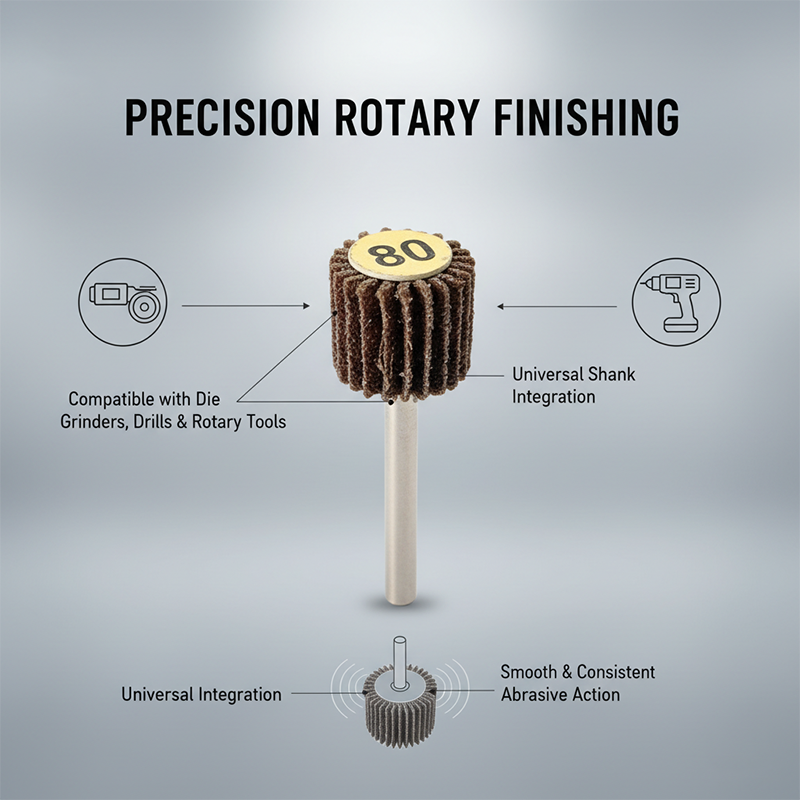
Цилиндрические лепестковые круги состоят из радиально расположенных абразивных лепестков вокруг цилиндрического сердечника и обычно устанавливаются через посадочное отверстие на финишные станки или специальные оправки.
Их «податливый» контакт обеспечивает снятие заусенцев, выравнивание риски, блендинг швов и доводку поверхности с хорошей «прощаемостью», не вызывая чрезмерного изменения размеров детали.
Описание продукта
Позиционирование продукта
Круги для финишной обработки плоскостей, наружных (OD) и внутренних (ID) диаметров
Цилиндрические лепестковые круги позиционируются как инструменты для доводки поверхности и блендинга с акцентом на равномерную риску и плавные переходы.
По сравнению с лепестковыми кругами на оправке они имеют большую площадь контакта и более ровный «ритм» процесса; по сравнению с лепестковыми дисками для УШМ лучше подходят для стабильной финишной обработки плоскостей, наружных (OD) и внутренних (ID) диаметров и профилированных поверхностей.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Технические характеристики
Конфигурации по посадочному отверстию, ширине, плотности и абразивной системе
|
Параметр |
Спецификация |
|
Тип продукта |
Цилиндрические лепестковые круги |
| Абразив |
Варианты абразива: AO / zirconia / ceramic |
|
Конструкция |
Радиальная лепестковая конструкция |
| Наружный диаметр |
Наружный диаметр 3/4″–12″ (20–300 мм) (возможно расширение) |
|
Ширина |
Ширина 3/8″–8″ (10–200 мм) (возможно расширение) |
| Посадочное отверстие |
Посадочное отверстие 1/4″–2″ (на заказ) |
|
Диапазон зернистости |
P60–P240 (возможно расширение) |
| Макс. об/мин (Max RPM) |
Маркировка по размеру и стандарту |
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Логика обработки
Податливый радиальный контакт — для равномерной риски и плавных переходов
Цилиндрические лепестковые круги формируют стабильную текстуру за счёт податливого контакта:
- Лепестки подстраиваются под небольшую кривизну и профиль;
- Непрерывная работа множества лепестков даёт равномерную и контролируемую риску;
- Они сильны в блендинге и доводке, а не в тяжёлом съёме.
Поэтому их часто используют для блендинга после сварки, переходов под «сатин/шлифованный» финиш, снятия заусенцев и лёгкого притупления кромки.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Конструкция основы и пределы применения
Финишная ориентация — не замена лентам или жёстким кругам
- Плюсы: Равномерный финиш, плавный блендинг, щадящий контакт с поверхностью
- Ограничения / пределы применения :Не для тяжёлого съёма и ударных режимов; для быстрого съёма используйте ленты или тяжёлые лепестковые круги/шлифкруги
Чрезмерный прижим или задержка на месте могут привести к перегреву и неравномерному износу — требуется стабильная подача
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Совместимость с оборудованием и условия работы
Круги с посадочным отверстием для финишных станков и производственной оснастки
- Оборудование: Финишные станки, полировально-шлифовальные машины, специальные оправки (установка через отверстие)
- Рекомендуемые условия: Средний–низкий прижим, стабильная окружная скорость, непрерывная подача
- Обязательно: Соответствие диаметра отверстия оправке, ширины круга и скоростного класса (не превышать Max RPM)
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Инженерное сравнение
|
Сравнение |
Цилиндрические лепестковые круги | Шлифовальные ленты | Нетканые круги |
| Способность к съёму материала | Низкий–средний | Высокая |
Низкая |
|
Стабильность риски |
Отличный | Хорошая (зависит от режимов) | Отличный |
| Блендинг | Отличный | Среднее–хорошее |
Отличный |
|
Влияние на размеры |
Низкая | Средний | Очень низкое |
| Типичное применение | Сатинирование/блендинг/снятие заусенцев | Выравнивание/съём |
Доводка/текстура |
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Типовые применения и отрасли
Стабильная финишная обработка металла, дерева и композитов
- Выравнивание «сатина» и блендинг на нержавейке/алюминии
- Блендинг швов, снятие заусенцев и лёгкое снятие фаски
- Доводка поверхности дерева/композитов (в зависимости от абразива)
- Непрерывная доводка фурнитуры, труб и профилей
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Диапазон зернистости и рекомендации по применению
Стратегия зернистости под финиш
Типовые рекомендации
- P60–P80: блендинг шва и поверхности (баланс)
- P100–P120: универсальное сатинирование и уточнение риски (самый распространённый)
- P150–P240: тонкий финиш, улучшение внешнего вида и исправление переделок
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Возможности OEM/ODM
Инженерная разработка кругов под производственный такт
OEM/ODM: стандарты наружного диаметра/ширины/посадки, плотность и жёсткость лепестков, угол укладки, абразивная система, материал сердечника и класс балансировки, упаковка и private label — инженерно под производственный такт и целевую текстуру.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Почему выбирают нас
Равномерный финиш требует балансировки, стабильной укладки и контроля процесса
Для стабильного финиша необходимы: динамическая балансировка, равномерная укладка лепестков, контроль системы связки и стабильность партий.Балансировка влияет на вибрации и равномерность риски; укладка и связка задают кривую износа.Мы проектируем под производственную стабильность, чтобы финиш был воспроизводимым.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Рекомендации по использованию и хранению
Лучший финиш достигается стабильной скоростью и подачей
- Не превышайте Max RPM; соблюдайте допустимые обороты и обеспечьте надёжный монтаж с правильной защитой
- Работайте со средним–низким прижимом и непрерывной подачей, чтобы избежать локального перегрева и неравномерного износа
- Для косметических деталей переходите по зернистостям ступенчато, чтобы уменьшить глубокую риску и переделки
- Храните в сухом месте в тени; избегайте влаги и сдавливания; после вскрытия повторно герметизируйте упаковку